
Using Geoengineering to Fight Global Warming: Saving the Planet on the Brink
Climatologists emphasize the need to cool the Earth as human activities have severely disrupted its energy balance. The problem of global warming is getting worse every year, and climate change is causing more and more destructive natural disasters. In 2023, the world recorded its first temperature increase of 1.52°C above pre-crisis levels, and greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise. According to some scientists, decarbonization alone is not enough to solve the climate crisis, and only geoengineering can offer a real solution, providing additional time for a just transition to a green economy.
Geoengineering: large-scale impact on nature in the fight against climate change
Geoengineering is the deliberate, large-scale manipulation of Earth’s natural systems to combat climate change. This field covers a variety of techniques that can be classified into two main categories: solar radiation management (SRM), known as solar geoengineering, and greenhouse gas removal (GGR) or carbon geoengineering.
Solar geoengineering aims to reflect some of the sun’s energy back into space, which helps lower temperatures and reduce the greenhouse effect. One method is albedo enhancement—increasing the reflectivity of clouds or the Earth’s surface to reflect more of the sun’s heat back into space.
For example, spraying seawater or creating air bubbles on the ocean surface has been proposed to increase the reflection of solar rays in remote marine areas.
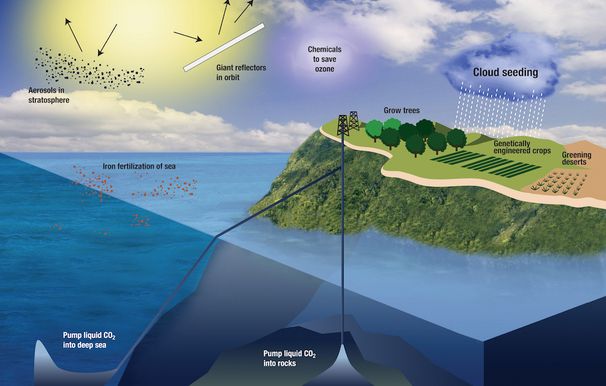
Another method is the use of space reflectors: placing special screens in orbit that reduce the amount of sunlight reaching Earth. The introduction of small reflective particles into the stratosphere is also being considered, which reflect sunlight, preventing it from reaching the earth’s surface.
Proponents of solar radiation management (SRM) argue that current levels of greenhouse gas emission reductions are insufficient to prevent the climate crisis and all possible solutions need to be considered. While the space shield would not be able to reduce greenhouse gas levels, it could prevent excessive heating by keeping pre-existing gases from releasing heat. However, critics warn that damage to such a screen could lead to a rapid and catastrophic rise in temperature.
Carbon Geoengineering Strategies: Innovative Approaches for Climate Stabilization
Carbon geoengineering involves techniques for removing carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases from the atmosphere to reduce the greenhouse effect and ocean acidification. To effectively combat climate change, such technologies need to be applied at a global level.
Carbon geoengineering methods include afforestation, which involves large-scale planting of trees; biochar production, where biomass is turned into coal and buried in the ground to prevent the carbon from returning to the atmosphere, for example by burying charcoal on agricultural land; and bioenergy with carbon capture and sequestration, in which biomass is grown and burned for energy and CO2 from emissions is captured.
Atmospheric air capture involves the use of special installations that extract carbon dioxide directly from the atmosphere and transfer it to another location for storage.

Ocean feeding involves adding nutrients to seawaters to stimulate the growth of organisms that absorb carbon dioxide. Improved weathering allows large quantities of minerals to come into contact with atmospheric carbon dioxide, followed by precipitation of the resulting compounds in the ocean or soil. There is also a method for increasing ocean alkalinity that involves dissolving rocks such as limestone, silicates or calcium hydroxide in seawater, increasing its ability to retain carbon and reducing acidification levels.
According to renowned climate scientist James Hansen, there is an urgent need to cool the planet as human activity has significantly disrupted the Earth’s energy balance, resulting in the planet receiving more heat from the Sun than it can radiate back into space.